Decoders are devices that assert the outputs according to input combinations. It outs all possible minterm combinations of 'n' number of inputs.
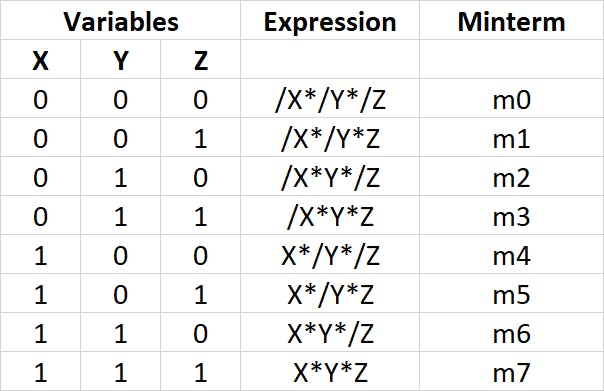
Quickly let's compile a minterm table for 3 variable combinations(X, Y, and Z),
Before plying the different decoder ICs and their nitty-gritty requirements, let's just build a three to eight decoder using some basic logic gates.
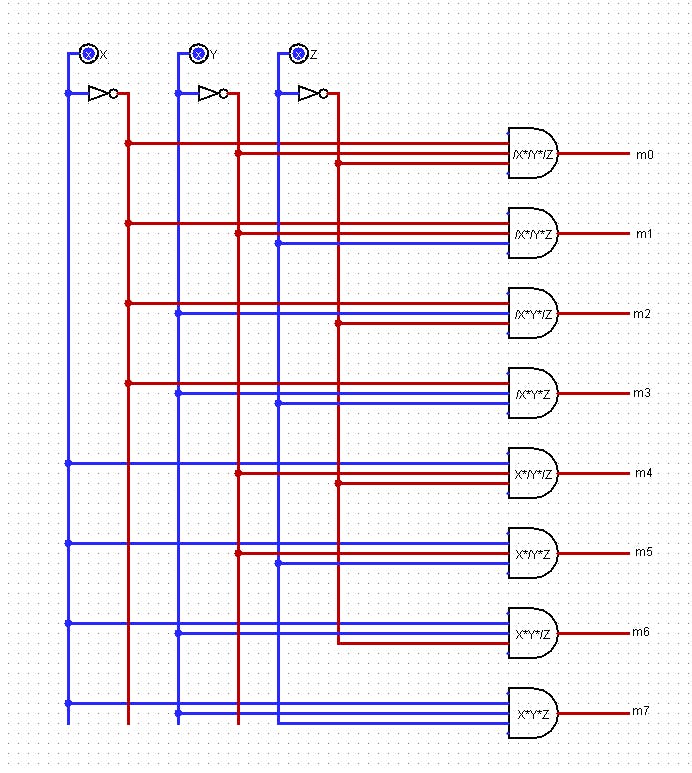
The boolean expressions evaluate the output states according to the input states ie.: X, Y, and Z. For instance, m0 is true(switched ON) only if X, Y, and Z are equal to 0 as /X/Y/Z = 1
Tidbit: 'OR' the outputs and you'll end up with the sum of products.
Now that we know how decoders work, there's a tad bit of theory we've to skim through to get comfortable with the IC jargon.
Integrated Circuit Switching Standards
Two major families of ICs are, TTL(Transistor-Transistor-Logic) and CMOS(Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor)
TTL Families: TTL-based ICs are based on Bipolar Junction Transistors. They are very fast and consume a lot of power.
CMOS Families: These ICs are based on Field-Effect Transistors. They consume lesser power(ideally zero). However, as a comeuppance, we've got to deal with high capacitance at their inputs. These days, the shortcomings are minimized to such an extent that the effects are negligible.
Myriads of sub-families have emerged and it isn't possible to go through all of them. Nevertheless, you could choose one as per your requirement.
Have a look at the different logic families here.
The IC Lingo
Interpreting TTL Datasheets
VCC(Supply voltage): The voltage required to drive the IC.
VOH(High-level output voltage): The minimum voltage output guaranteed when outputting a logic HIGH.
VOL(Low-level output voltage): The maximum voltage output guaranteed when outputting a logic LOW.
VIH(High-Level Input Voltage): Minimum input voltage required to act for logic HIGH.
VIL(Low-Level Input Voltage): Maximum input voltage required to act for logic LOW.
IOH(High-Level output current): The maximum amount of current, the IC can source when driving a logic HIGH.
IOL(Low-Level output current): The maximum amount of current, the IC can sink when driving a logic LOW.
IIH(High-Level input current): The amount of current required to drive the input to logic HIGH.
IIL(Low-Level input current): The amount of current required to drive the input to logic LOW.
TPHL(Propagation delay from input to output for a HIGH to LOW transition): Consider an IC being driven HIGH and the input instantaneously changes to LOW. There's a finite amount of time taken for this to take effect called the propagation delay(usually in nanoseconds).
TPLH(Propagation delay from input to output for a LOW to HIGH transition): Consider an IC being driven LOW and the input instantaneously changes to HIGH. There's a finite amount of time taken for this to take effect called the propagation delay(usually in nanoseconds).
FMAX(Maximum switching frequency): For clock synchronized ICs, this is the fastest it can be clocked at for it to stay reliable.
TA(Temperature Ambient): The range of ambient air temperatures the IC can operate at.
Interpreting CMOS Datasheets
VCC(Supply voltage): The voltage required to drive the IC.
VOH(High-level output voltage): The minimum voltage output guaranteed when outputting a logic HIGH.
VOL(Low-level output voltage): The maximum voltage output guaranteed when outputting a logic LOW.
VIH(High-Level Input Voltage): Minimum input voltage required to act for logic HIGH.
VIL(Low-Level Input Voltage): Maximum input voltage required to act for logic LOW.
FANOUT: Since CMOS chips replace TTL in most of the modern circuit designs; fanout's a standard used to fathom the output ability of a CMOS chip. Most of them have a fanout of 8-20, meaning a single CMOS chip can drive 8-20 TTL inputs.
II(Input Leakage Current): The amount of current a CMOS chip, sources, or sinks due to leakage(usually in the order of nano amperes).
CI(Input Capacitance): The amount of input capacitance a CMOS chip has. This factor takes a toll on the input signals.
CL(Load Capacitance): The amount of capacitance a CMOS output can drive.
TPHL(Propagation delay from input to output for a HIGH to LOW transition): Consider an IC being driven HIGH and the input instantaneously changes to LOW. There's a finite amount of time taken for this to take effect called the propagation delay(usually in nanoseconds).
TPLH(Propagation delay from input to output for a LOW to HIGH transition): Consider an IC being driven LOW and the input instantaneously changes to HIGH. There's a finite amount of time taken for this to take effect called the propagation delay(usually in nanoseconds).
FMAX(Maximum switching frequency): For clock synchronized ICs, this is the fastest it can be clocked at for it to stay reliable.
TA(Temperature Ambient): The range of ambient air temperatures the IC can operate at.
Active LOW and Active HIGH
Active LOW logic: The device performs its required operation when the logic level is LOW. Most of the ICs used in digital designs are Active LOWs.
Active HIGH logic: The device performs its required operation when the logic level is HIGH.
Implementing Decoders
A commonly used Active LOW Decoder IC is 74XX138, and "XX" refers to the logic family. Over time as you work on more and more designs, something that becomes a habit is going through datasheets. I shall be using the 74F138N decoder IC by Philips and here's the link to its datasheet.
Circuit Design: The software used to design is, Labcenter Proteus 8 professional, fairly simple, and powerful software that comes in handy whenever you wanna design a circuit.
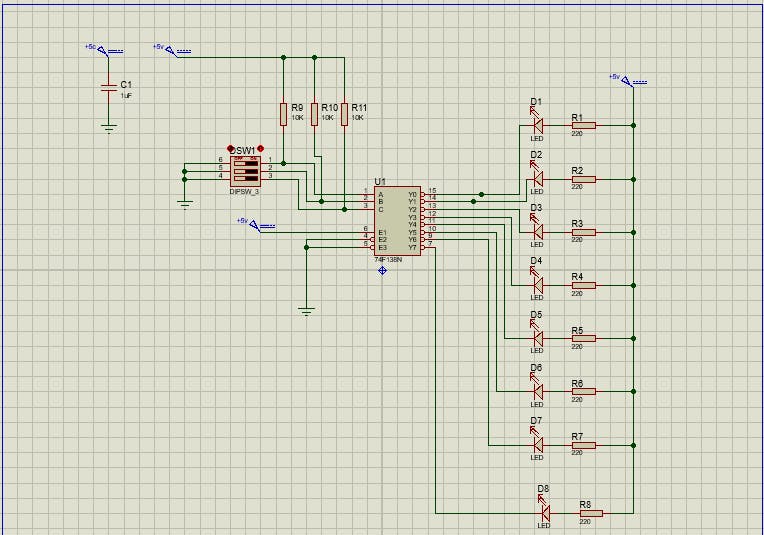
When working with ICs, make it a habit to use decoupling capacitors. Here's an article about it.
Working
A word of caution, the circuit put together on the breadboard isn't ideal. Use wires of appropriate size as longer wires may cause all kinds of noise and disturbances.
References:
1) Andre' LaMothe. Design your own video game console: Combinational Logic and SSI/MSI Blocks, Entering the Digital Realm.
2) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logic_family

